Numantia destruction in 133 BC. and the control of Celtiberia by Roma did not call a halt to the quarrels with Indigenous, the abusive administration of Rome caused insurrections of Celtiberians and Lusitanians in 114 BC., later, in 98 BC.; T. Didius was uncharged to put down this last insurrection subjecting among other cities Termes (Montejo de Tiermes, Soria) in the year 97 BC.Later, the Celtiberian peoples took advantage from the civil war of Roma between the supporters of Mario and Sila, were on Sertorius (Mario follower) who support Indigenous tribes triggered the wars known as Sertorian wars (from 82 to 72 BC.). Pompey, in charge of government of Hispania Citerior, attacked Numantia and Uxama (Osma) in 76 BC., among other cities, snatched Celtiberia control to Sertorius.According to Appian, Scipio surrendered the city and its territory to those Indigenous peoples who had helped him to conquest Numantia.
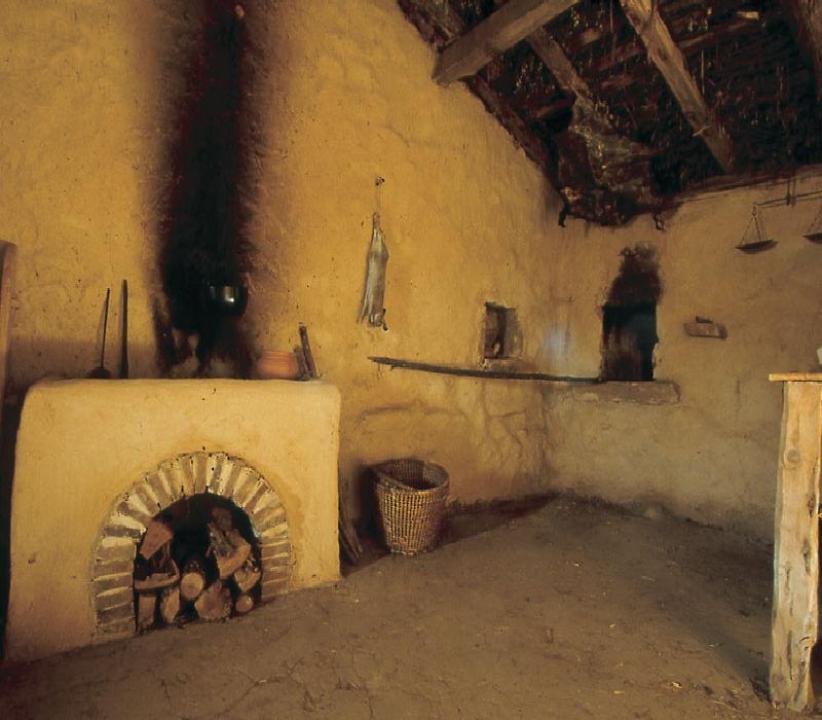
The study of the plan of old excavations in Numantia allow demarcating the perimeter of a previous occupation, in particular in South zone, reflected in a semicircular extension parallel to a previous city that corresponds to the closing of the wall city of which part of its route is known.The occupied surface approached to 9 hectares that is something bigger than the old city. This second city presents irregular streets in its execution and plan. The streets were paved with stones of uneven size. In the stream there are big raw stones without any regularity which were used as stepping-stone from a sidewalk to another. The planning of this city is the result of the adaptation of the Indigenous initial plan to the following extension and city necessities in the course of the 1st century BC.